This is a preview of updates coming to the Technical Bulletin's website in April 2026. Return to current site.
Read more about the modernization release schedule in this announcement.
Comment via the yellow feedback button in the lower right hand corner of the page. Contact the NLM Help Desk with any questions or concerns.
This is archived content.
Links may have become inactive over time. Visit Archive-It to find the original published layout.
PubMed® Notes for 2007
Nahin A. PubMed® Notes for 2007. NLM Tech Bull. 2006 Nov-Dec; (353):e5.
December 05, 2006 [posted]
The following notes explain how PubMed® or searching with PubMed may be affected by changes to MEDLINE® or MeSH® vocabulary for the 2007 system, some of which has been described in the articles listed under Additional Information in the box to the right. Searchers are advised to consider any stored strategies, e.g., My NCBI saved searches, URL links to PubMed, and RSS feeds, which may need to be revised.
- The Limits page menu for "Type of Article" was modified to include nine new Publication Types, including Comparative Study. These MeSH terms were treated as headings until this year.
- The status tag for OLDMEDLINE records has changed from [PubMed - OLDMEDLINE for pre1966] to [PubMed - OLDMEDLINE].
- The option for OLDMEDLINE was removed from the Limits "Subsets" menu. The reduced number of citations in this subset and the growing number of older citations being added to PubMed that are not part of the OLDMEDLINE project, have lessened the value of this subset as a limit for searching. The direct search, oldmedline [sb], can still be used.
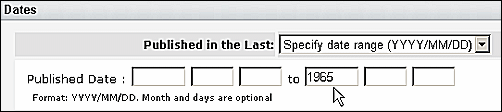
To limit to older citations, use the Dates section in Limits. Select "Specify date range" on the "Published in the Last:" menu. It is only necessary to enter the latest date of interest (see Figure 1).
- A new type of Comment/Correction notation has been added to PubMed citations to indicate when an article has been partially retracted. Citations for the partial retraction will display the note, Partial retraction of, followed by citation information for the article being partially retracted. The citation for the article being partially retracted will have the notation, Partial retraction in, followed by citation information. Whenever possible, there will be links between the related citations.
See the chart below for Comment/Correction types, and search and display information effective with the implementation of the 2007 system in mid-December 2006.
Comment Correction Type Search as MEDLINE Display Field Tag Comment in: hascommentin CIN Comment on: hascommenton CON Erratum in: haserratumin EIN Erratum for: haserratumfor EFR Corrected and republished in: hascorrectedrepublishedin CRI Corrected and republished from: hascorrectedrepublishedfrom CRF Retraction in: hasretractionin RIN Retraction of: hasretractionof ROF Partial retraction in: haspartialretractionin PRIN Partial retraction of: haspartialretractionof PROF Update in: hasupdatein UIN Update of: hasupdateof UOF Summary for patients in: hassummaryforpatientsin SPIN Original Report in: hasoriginalreportin ORI Republished in: hasrepublishedin RPI Republished from: hasrepublishedfrom RPF
- MUID (MEDLINE Unique Identifier) data has been removed from records. The PMID remains as the unique identifier for PubMed records.
-
Print dates of publication and electronic dates of publication can now be searched independently of one another. The search tag for print publication date is [ppdat] and the search tag for electronic publication date is [epdat]. The standard PubMed date format, YYYY/MM/DD, should be used. Ranging is also available.
Examples:
2006/01 [ppdat]
2005/10/01:2006/09/30 [epdat]
Please be aware that the recommended method for publication date searching remains using the Date of Publication (found on PubMed's Limits screen, or with the search tag, [dp], for direct searching) as it includes both print and electronic dates (see PubMed Help). These new options are available to assist users creating queries for LinkOut resource files.