This is a preview of updates coming to the Technical Bulletin's website in April 2026. Return to current site.
Read more about the modernization release schedule in this announcement.
Comment via the yellow feedback button in the lower right hand corner of the page. Contact the NLM Help Desk with any questions or concerns.
This is archived content.
Links may have become inactive over time. Visit Archive-It to find the original published layout.
Recent Updates Clarifying PubMed Central's Role as an Archive
Recent Updates Clarifying PubMed Central's Role as an Archive. NLM Tech Bull. 2023 Mar-Apr;(451):e7.
April 19, 2023 [posted]
PubMed Central (PMC) has a large and diverse user base that includes students and the public, as well as researchers, clinicians, and librarians. PMC recognizes that these different audiences have varying levels of familiarity with NLM, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the scholarly publishing process and has recently made updates to how articles are described, displayed, and shared in PMC to provide users with more context.
Here are the updates made to PMC:
A prominent note has been added to all PMC article pages to clarify the relationship of NLM to the articles it collects and archives in PMC. This update to the article display, as well as other contextual information, is also now more visible to all users by defaulting mobile users to the same article view ("Classic view") as desktop users. The previous default view on mobile, PubReader, is still available as an option on article pages under "Other Formats."
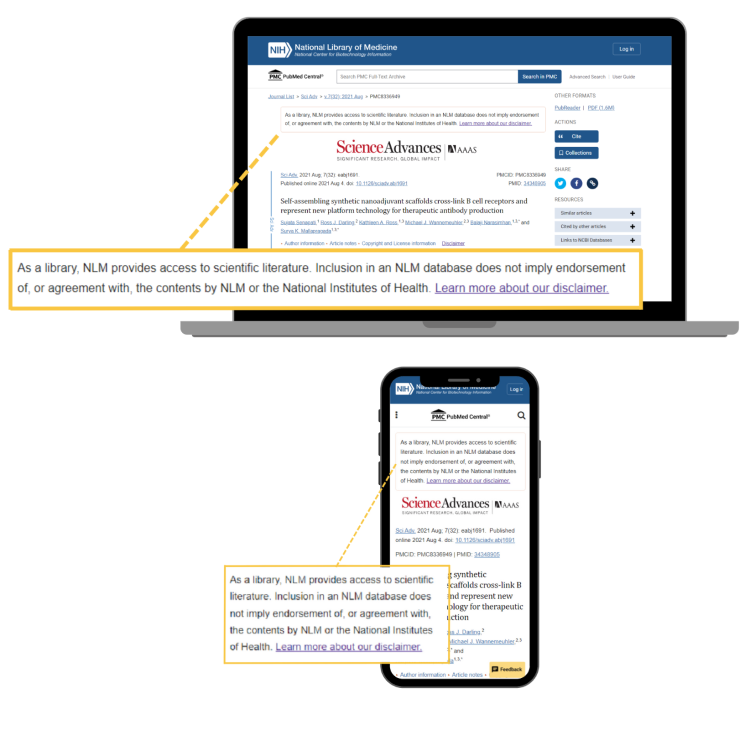
Figure 1: New contextual note appears above PMC articles on the desktop and mobile sites.In line with this article display update, NLM is also updating the default social media display when articles from PMC are shared to include additional context. This change will be reflected on social media platforms in the coming weeks.

Figure 2: New contextual note that will display when PMC articles are shared on social media.A new infographic has been added to the PMC Overview, Author Manuscripts, and NIH Preprint Pilot webpages, which show the different types of content that are in PMC and how each fits into the scholarly publishing process. The nearly 9 million articles in PMC span the scholarly publishing cycle, including those that have been formally published in a scholarly journal, author manuscripts that have been peer-reviewed and accepted for publication in a journal, and preprint versions of articles that have been made public prior to peer review. This content is deposited in the PMC archive through collaborations with publishers, societies, research funders, and international organizations. (See our Collections page for an overview of the results of these content collaborations.)
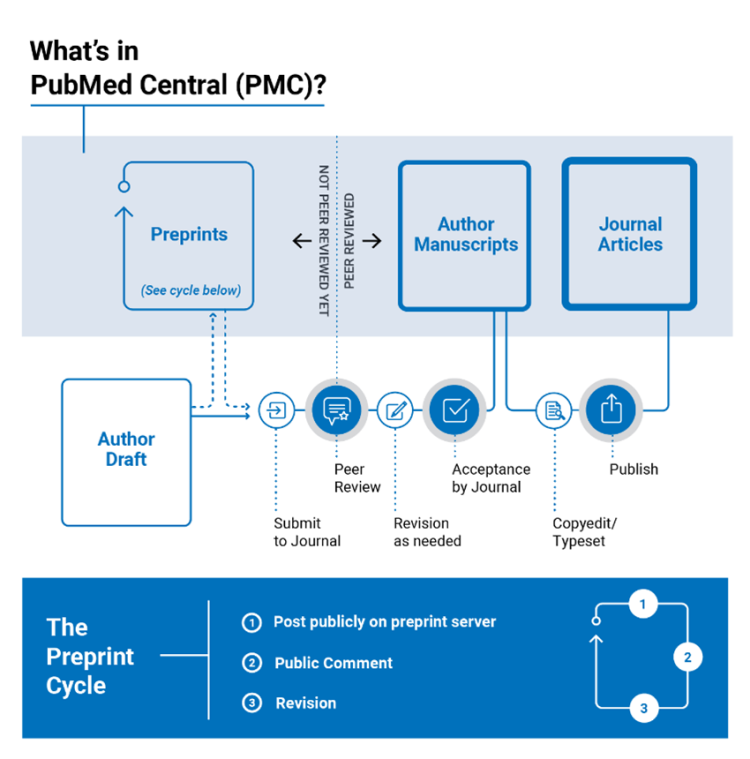
Figure 3: Updated infographic that clarifies how PMC content fits within the scholarly publishing process.
Questions?
As always, if you have any questions or comments about PMC, you can email us at pubmedcentral@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov or leave feedback on the yellow feedback button on the site.


